Supervised Classification
Supervised classification involves training a model on a labeled dataset and using it to predict the labels of new data. The model learns the relationship between the input features and the output labels during training, allowing it to make informed predictions on unseen data.
Class labeling
In supervised classification, each data point is associated with a specific class label. These labels are used during the training process to teach the model how to differentiate between different classes based on the input features.
Important
Changes in this view will impact the supervised classification results. If models have already been trained, a popup will appear, asking if you want to delete the existing models, or cancel the changes. If you choose to delete the models, you will need to retrain them after making changes in this view.
Unclassified Class
The Unclassified class is a default class that is always present in the view. It serves as the initial container for samples that have not yet been categorized into other classes.
It is also the class used as sample class in multi-class classification, see Multi-Class Classification Algorithms.
Note
Any new samples added to the dataset will automatically be placed in the Unclassified class, and therefore will not influence the trained models, but will be taken into account during the classification scoring.
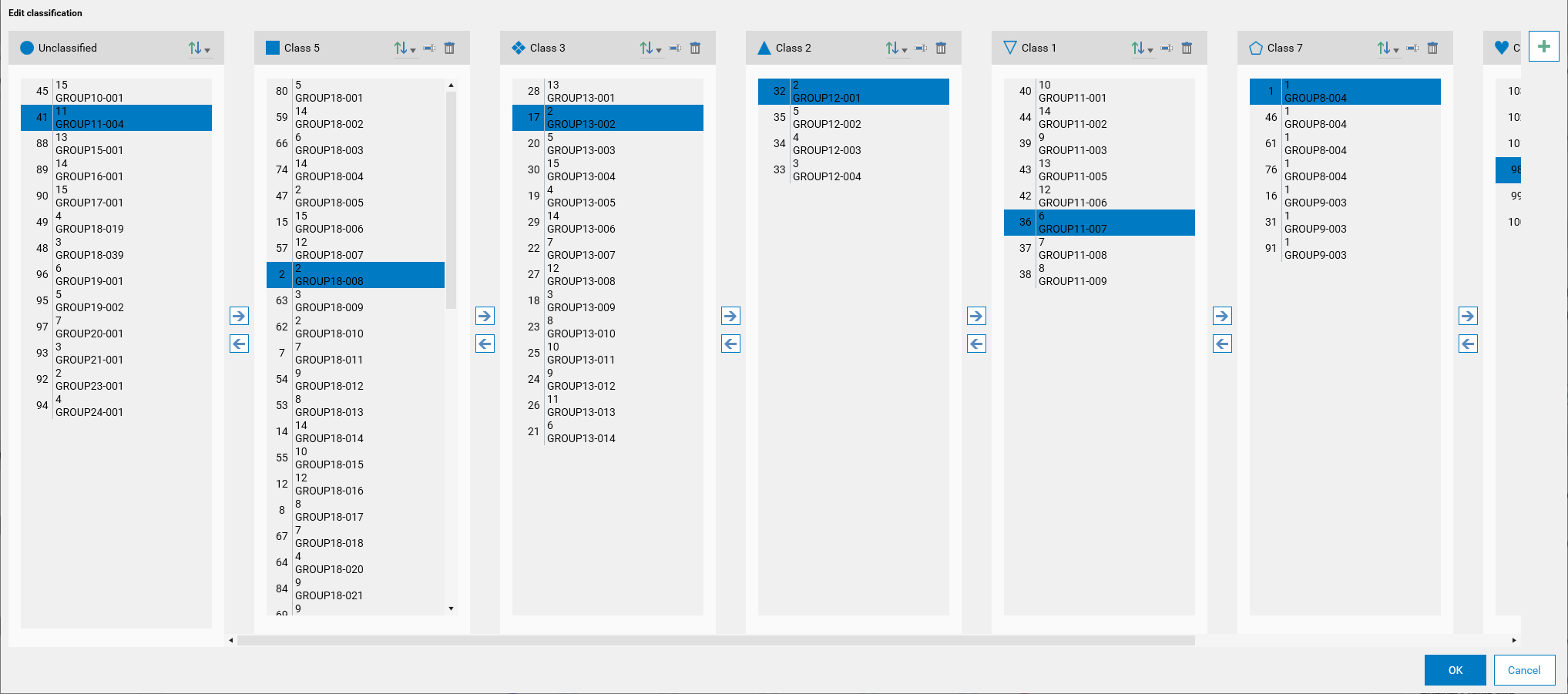
User-Defined Classes
Users have the ability to create, rename, and delete additional classes apart from the Unclassified class. These classes can be customized according to the user’s needs.
Important
Changing a user-defined class, or assigning (or removing) samples to it, will impact the trained models. A popup will appear, asking if you want to delete the existing models, or cancel the changes. If you choose to delete the models, you will need to retrain them after making changes in this view.
Adding classes
To add a new class, users can click on the  button. This will create a new class, and the name can be edited directly in the class list.
button. This will create a new class, and the name can be edited directly in the class list.
Moving Samples
Samples can be moved between classes using one of the following methods, after selecting one or more samples:
Arrow Buttons: Use the arrow buttons (
 or
or  ) to move samples from one class to another.
) to move samples from one class to another.Drag and Drop: Users can drag samples from one class and drop them into another class for easy reorganization.
Sort Options
The view provides various sorting options to organize samples within each class. Users can sort samples based on different criteria by clicking on the  button and selecting one of the following options:
button and selecting one of the following options:
Sort by position 1-9
Sort by position 9-1
Sort by name A-Z”
Sort by name Z-A”
The sorting options help users quickly find and organize samples within the classes. It does not impact the classification of the samples, but rather provides a convenient way to manage the samples visually.
Rename
To rename a class, users can click on  button. This will allow them to edit the name directly. After editing, pressing
button. This will allow them to edit the name directly. After editing, pressing  or clicking on
or clicking on  will save the new name, clicking on
will save the new name, clicking on  will cancel the edition.
will cancel the edition.
One-Class
One-class classification, also known as unary classification, is a type of classification problem where the goal is to identify members of a specific class among all other possible instances. In this scenario, the model is trained to recognize examples of a single class, distinguishing them from all other instances that do not belong to that class.
Key Characteristics:
Single Class Focus: The model is trained to identify instances of one particular class.
Anomaly Detection: Often used for anomaly detection, where the class of interest is the “normal” class, and any deviation is considered an anomaly.
Imbalanced Data: Useful in situations where the data is highly imbalanced, with a majority of instances belonging to one class.
In-depth information on one-class classification algorithms can be found in the training section: One-Class Classification Algorithms.
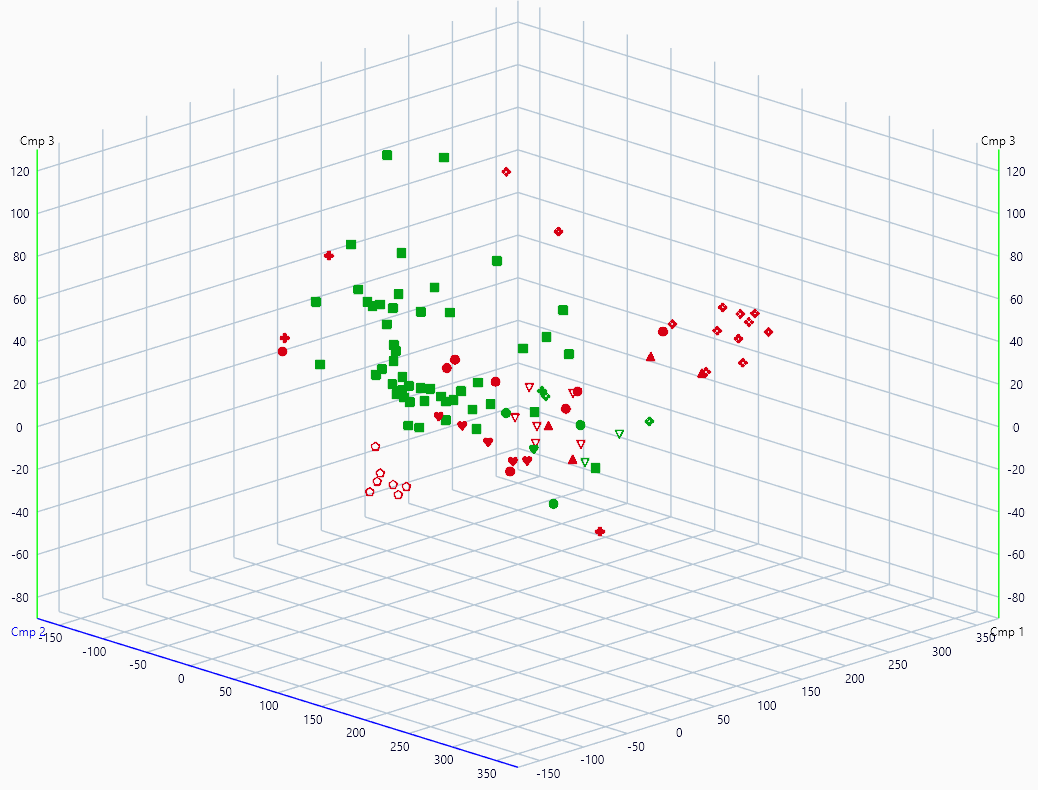
Results preview
The 3D View will use the same color scheme, where tracks fitting the class are shown in green and those not fitting are shown in red.
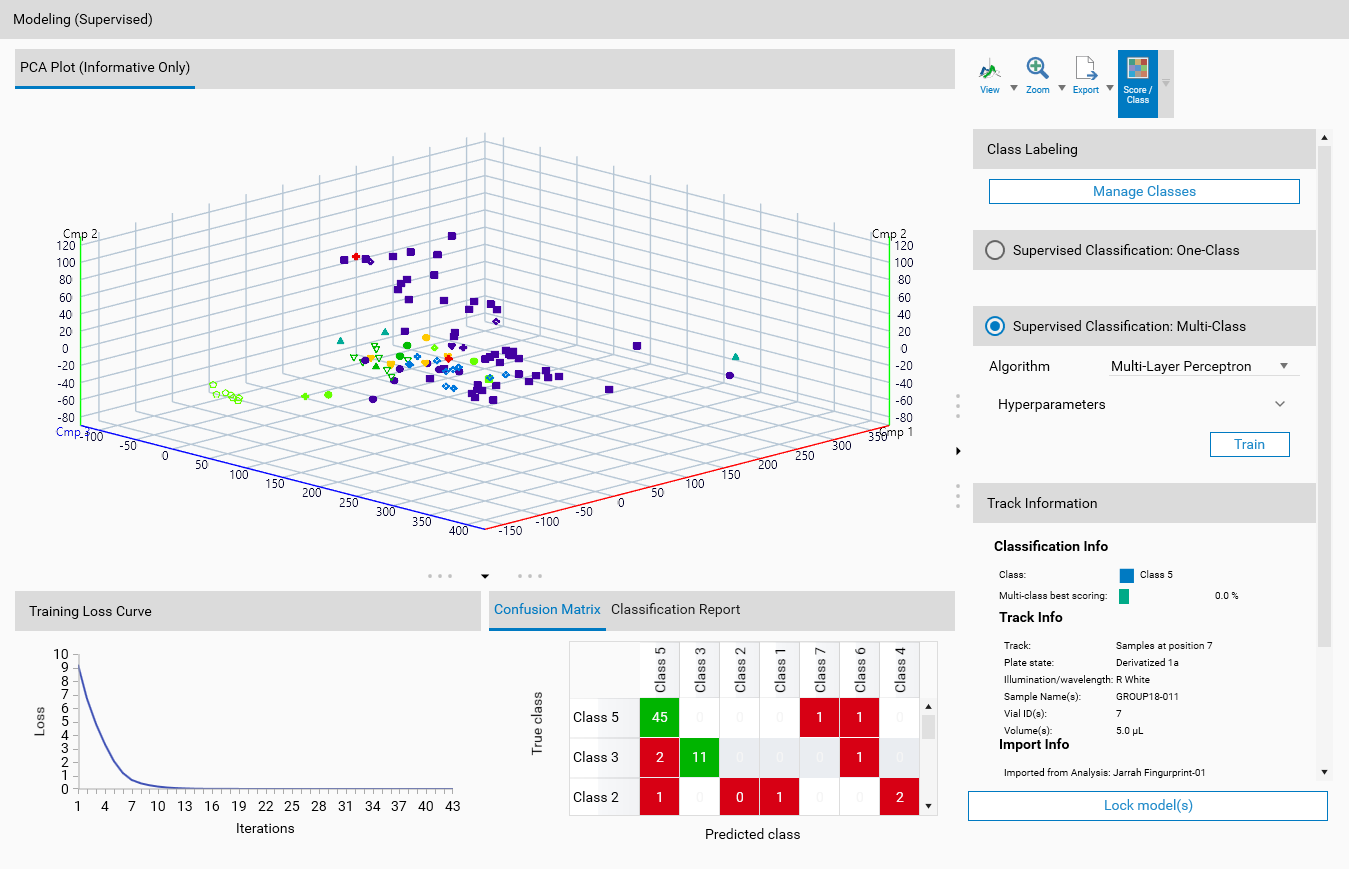
Multi-Class
Multi-class classification involves classifying instances into several classes.
Key Characteristics:
Multiple Classes: The model is trained to distinguish among several classes.
Class Labels: Each instance in the dataset is labeled with one of the multiple classes.
Decision Boundaries: The model learns decision boundaries that separate the different classes in the feature space.
In-depth information on multi-class classification algorithms can be found in the training section: Multi-Class Classification Algorithms.
Results preview
By default, the 3D View will display a color for each class, the highest probability of belonging to a class will be used to color the track. Corresponding classes’ color will be displayed in the Overview.
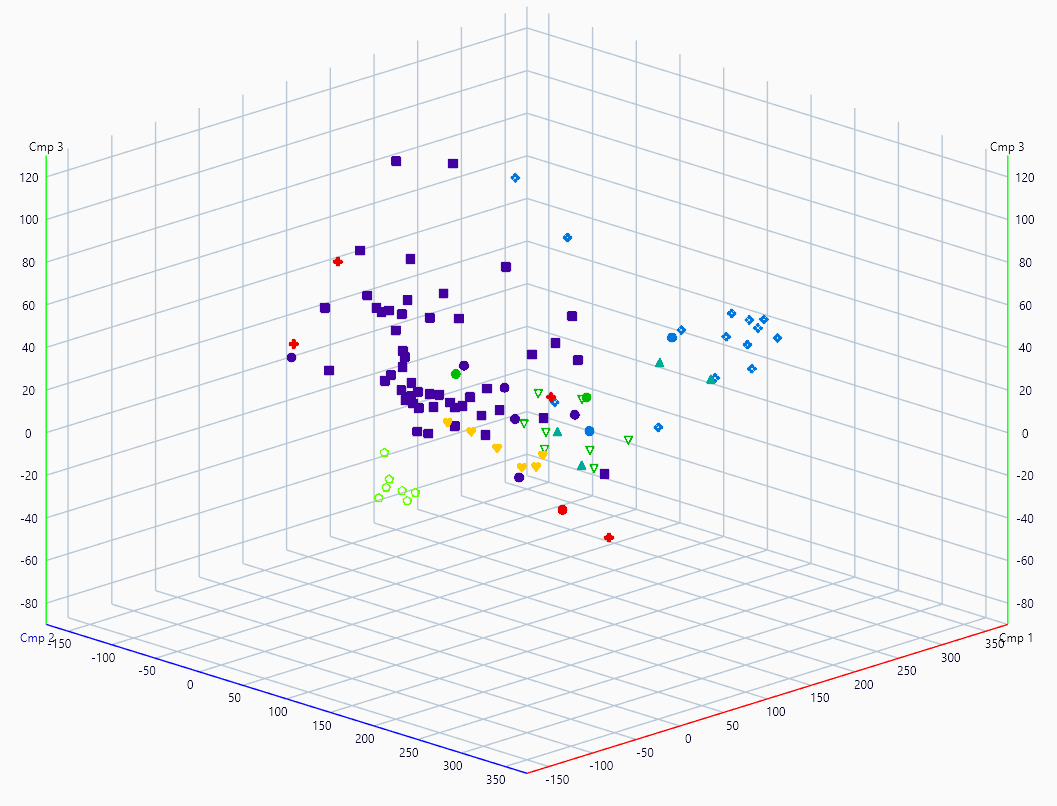
The corresponding Overview will be:
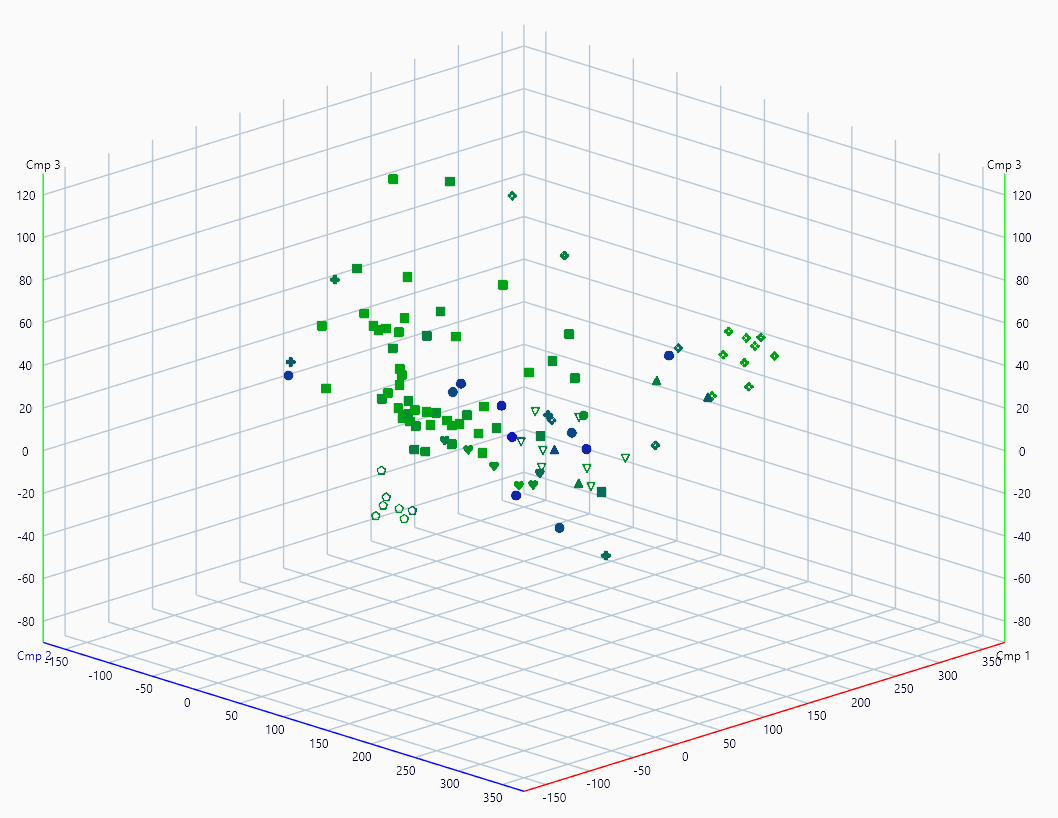
The 3D View can use the same color scheme as the result table, where tracks are colored based on the highest probability of belonging to a class. The switch is done via  . If a track has a high probability for multiple classes, it will be displayed in a mixed color.
. If a track has a high probability for multiple classes, it will be displayed in a mixed color.
Locking model(s)
When one or both type of models are trained, it is possible to lock them to prevent any accidental modification or deletion. This is done by clicking on the Lock mode(s) button. Once locked, the button will change to Unock mode(s), indicating that the model(s) is (are) protected. Also the date and time of the locking will be displayed next to the button.